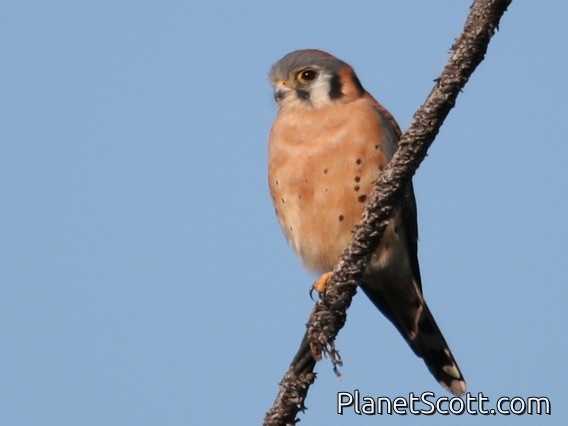
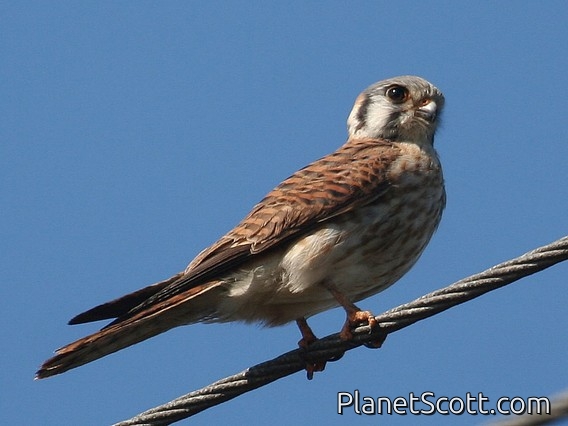
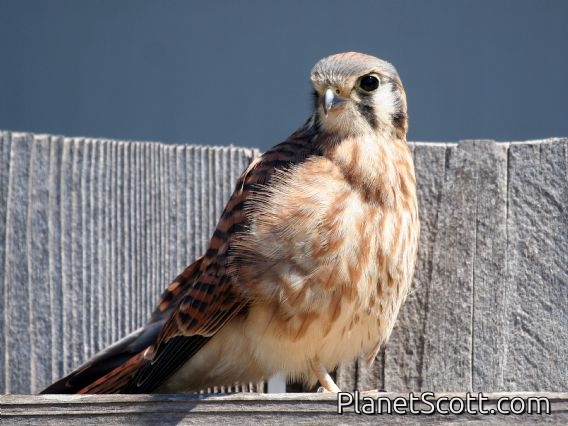
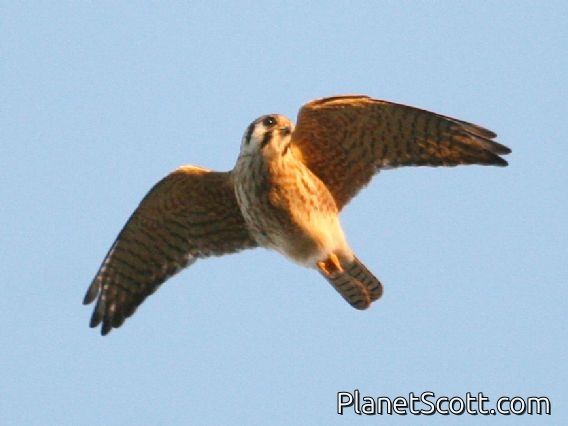
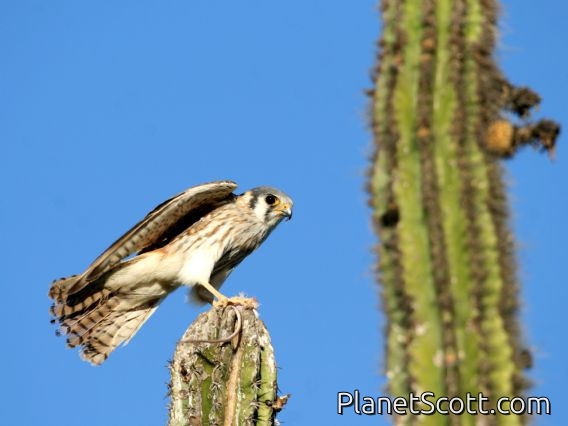
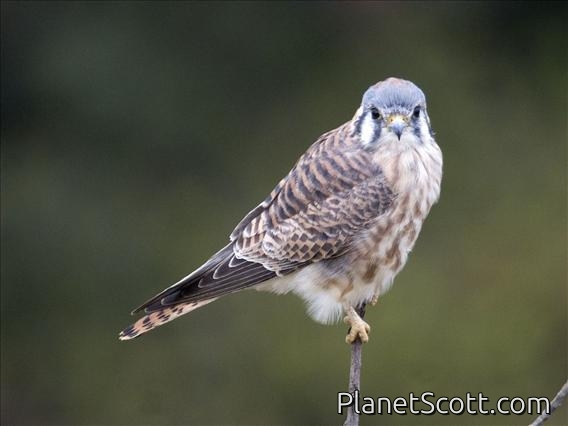
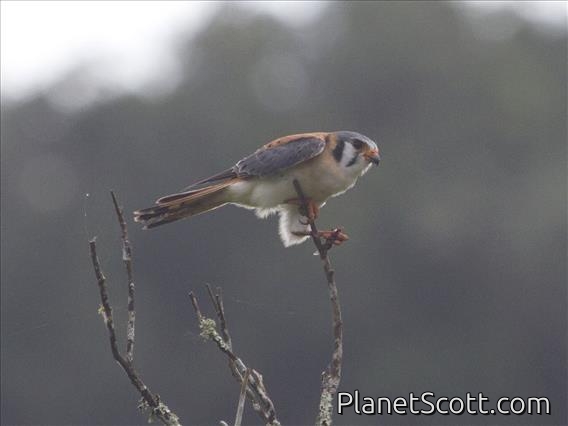
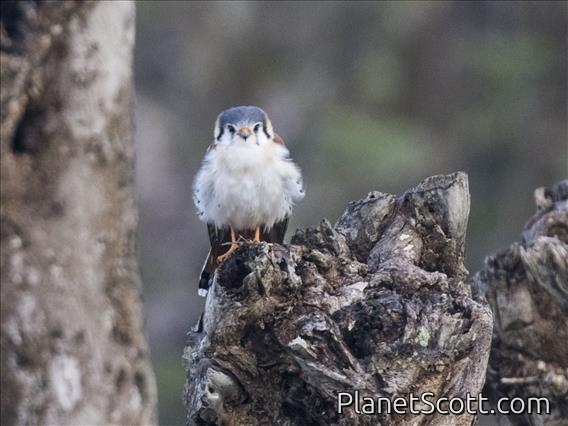
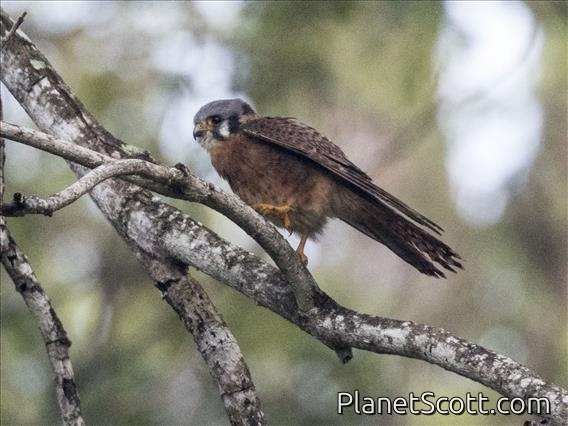
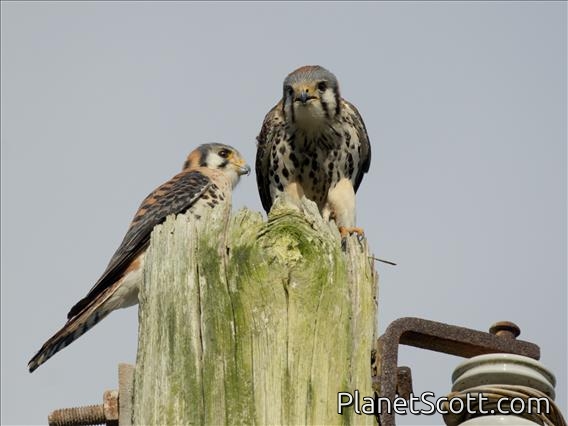
American Kestrel (Falco sparverius)
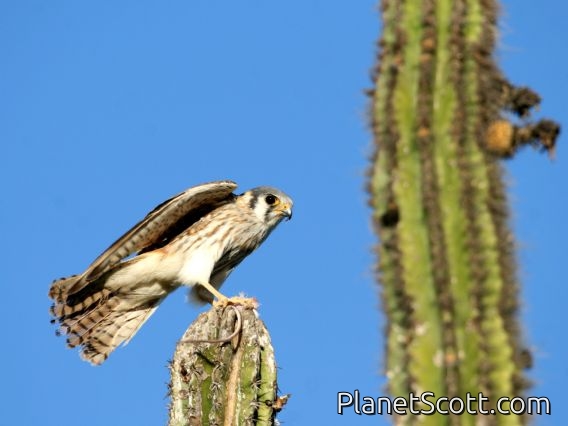
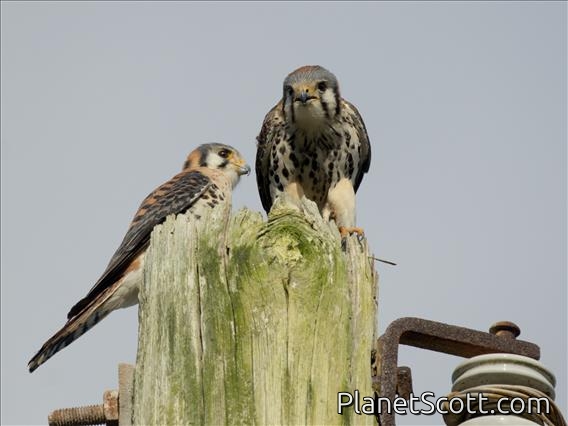
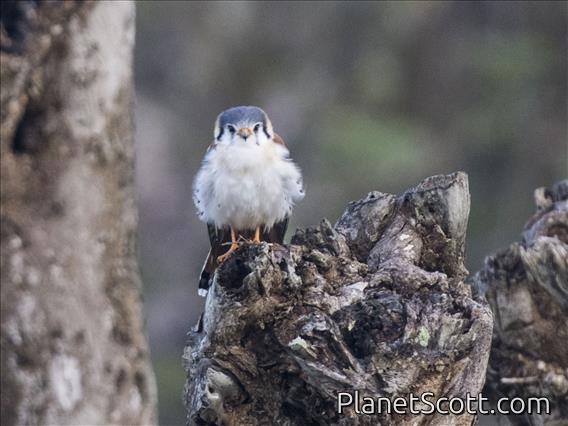
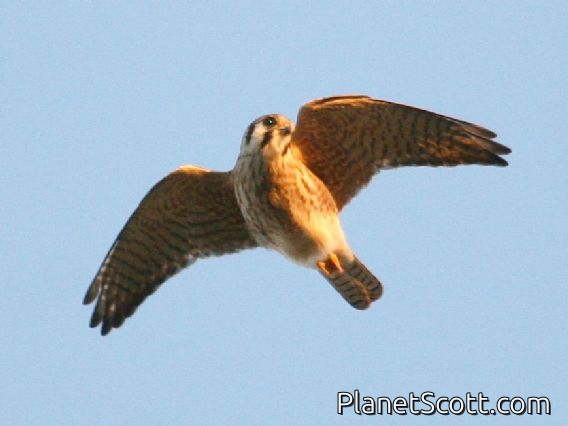












About American Kestrel (Falco sparverius)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Pelicans
- Family: Falcons and Caracaras
The American kestrel is the smallest and most common falcon in North America. Though it has been called the American sparrowhawk, this common name is a misnomer; the American kestrel is a true falcon, while neither the Eurasian sparrowhawk nor the other species called sparrowhawks are in the Falconidae family, hence only very distantly related to the American kestrel. It has a roughly two-to-one range in size over subspecies and sex, varying in size from about the weight of a blue jay to a mourning dove. It also ranges to South America and is a well-established species that has evolved into 17 subspecies adapted to different environments and habitats throughout the Americas. It exhibits sexual dimorphism in size and plumage, although both sexes have a rufous back with noticeable barring. Its plumage is colorful and attractive, and juveniles are similar in plumage to adults.
Source: Wikipedia
Trips
Visits
-
2002-11-01
Lost Coast, United States of America× -
2005-12-06
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2006-02-14
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2006-06-20
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2006-07-01
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2006-11-17
Quilatoa, Ecuador× -
2007-01-05
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2007-04-11
San Diego Estuary, United States of America× -
2007-10-14
Ixhuacan de los Reyes, Mexico× -
2007-12-07
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2008-01-10
Laguna Quelela, Mexico× -
2008-02-24
San Jose del Cabo - Airport Wash, Mexico× -
2008-12-06
Suisun Marsh, United States of America× -
×
-
2009-10-12
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2009-11-29
Heron's Head Park, United States of America× -
2010-02-20
Coatepec, Mexico× -
2010-10-30
Miller Meadow Forest Preserve, United States of America× -
2011-05-29
Del Puerto Canyon and Mines Road, United States of America× -
2011-07-25
Praia do Forte, Brazil× -
2011-10-08
Crabtree Nature Center, United States of America× -
2012-06-25
Bernal Hill, United States of America× -
2012-07-08
Necedah NWR, United States of America× -
2012-07-09
Sax-Zim Bog, United States of America× -
2012-07-10
170th St , United States of America× -
2012-07-10
Chase Lake NWR, United States of America× -
2012-07-11
Theodore Roosevelt National Park - South Unit, United States of America× -
2012-09-07
Heron's Head Park, United States of America× -
2012-09-09
Coachella Valley Preserve, United States of AmericaDid not get a great look at the kestrel, and it could have been another type of falcon.× -
2012-09-23
Heron's Head Park, United States of America× -
2012-10-08
Presidio - El Polin Spring, United States of America× -
2012-12-06
Solano County Farmlands, United States of America× -
2013-07-02
Yolla Bolla Wilderness, United States of America× -
2014-01-19
Santo Domingo - El Embajador Hotel Grounds, Dominican Republic× -
2014-01-21
Puerto Escondido, Dominican Republic× -
2014-01-21
Jimani, Dominican Republic× -
2014-01-22
El Aceitillar, Dominican Republic× -
2014-01-26
Los Haitises National Park, Dominican Republic× -
2014-02-22
Panoche Valley, United States of America× -
2014-03-09
Hahamongna Watershed Park, United States of America× -
2014-06-07
Sunol Regional Wilderness--Visitor Center area, United States of America× -
2014-06-14
Peaarson-Arastradero Preserve, United States of America× -
2014-09-20
McNear Brick and Block, United States of America× -
2015-01-02
Pixley NWR, United States of America× -
2015-01-04
Del Puerto Canyon and Mines Road, United States of America× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
2019-06-26
Arica, Chile× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
××
-
×
-
2024-04-06
Laguna de Sanchez, Mexico× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
2025-12-30
Yosemite Slough, United States of America×