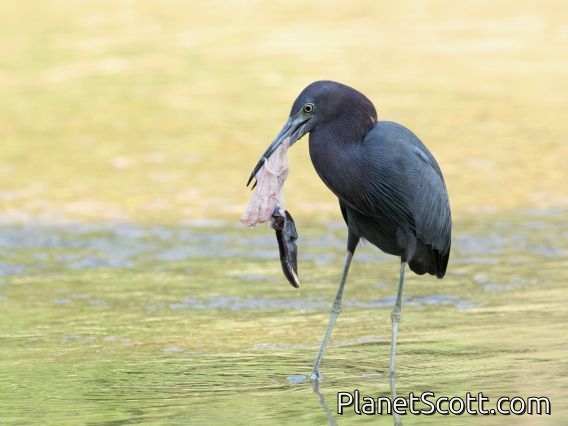
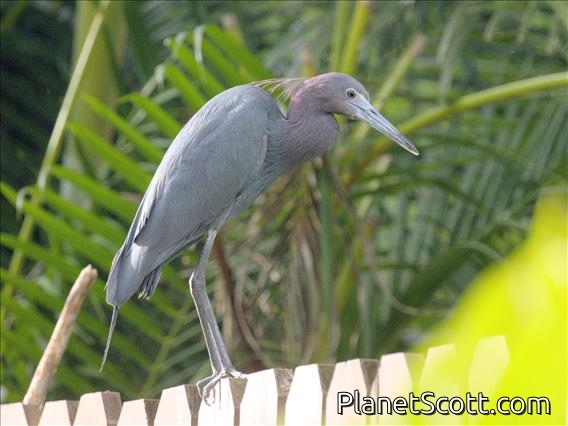
Little Blue Heron (Egretta caerulea)
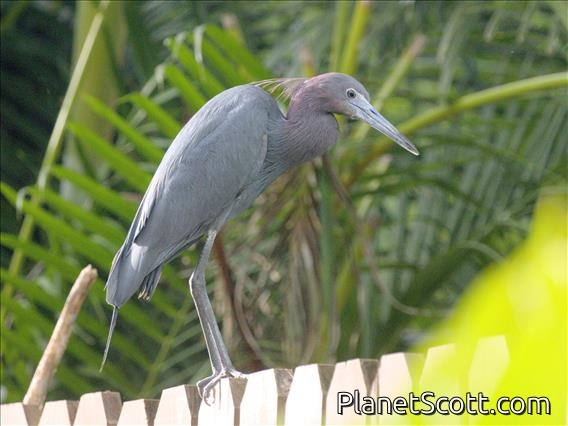

Little Blue Heron (Egretta caerulea)
×


Little Blue Heron (Egretta caerulea)
About Little Blue Heron (Egretta caerulea)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Pelicans
- Family: Herons
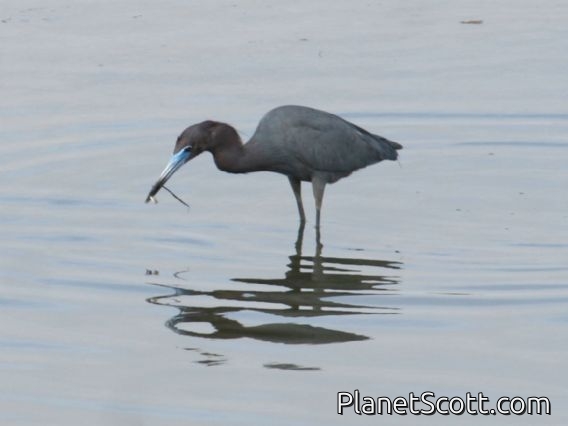
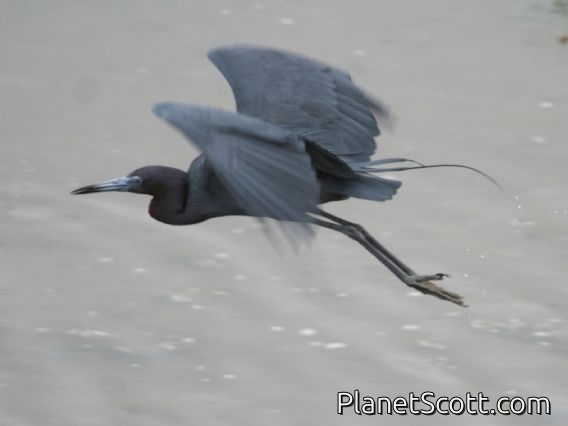
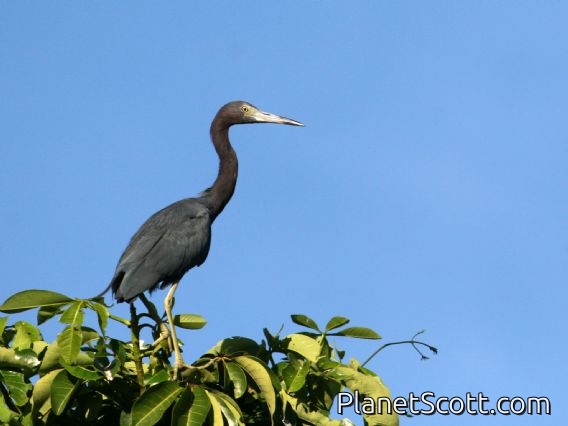
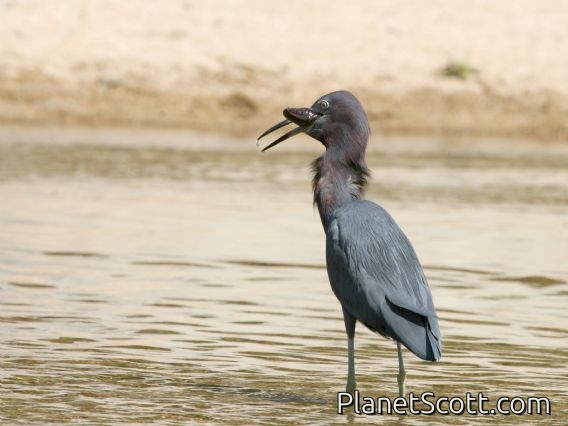
The little blue heron is a small heron of the genus Egretta. It is a small, darkly colored heron with a two-toned bill. Juveniles are entirely white, bearing resemblance to the snowy egret. During the breeding season, adults develop different coloration on the head, legs, and feet.
Source: Wikipedia
Trips
Visits
-
2001-03-08
Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, United States of America× -
2007-04-11
San Diego Estuary, United States of America×× -
2007-10-11
La Mancha, Mexico× -
2007-10-17
Sontecomapan, Mexico× -
2008-01-04
Puerto Vallarta, Mexico×× -
2008-01-07
La Tovara, Mexico× -
2009-01-18
Lamanai Ruins River Trip, Belize× -
2009-02-07
Parque National Iztopo, Honduras× -
×
-
2009-02-18
Parque National Palo Verde, Costa Rica× -
2009-02-24
Corcovado National Park - Los Patos, Costa Rica× -
2009-02-25
Corcovado National Park - La Sirena, Costa Rica× -
2009-03-15
Boca de Cupe, Panama× -
2011-07-10
Santa Fe River, United States of America× -
2013-04-14
Austin, United States of America× -
2013-04-16
Aransas NWR (CTC 037) (Aransas Co.), United States of America× -
2013-04-17
Brazoria NWR (UTC 108), United States of America× -
2014-01-21
Jimani, Dominican Republic× -
2014-01-26
Los Haitises National Park, Dominican Republic× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×