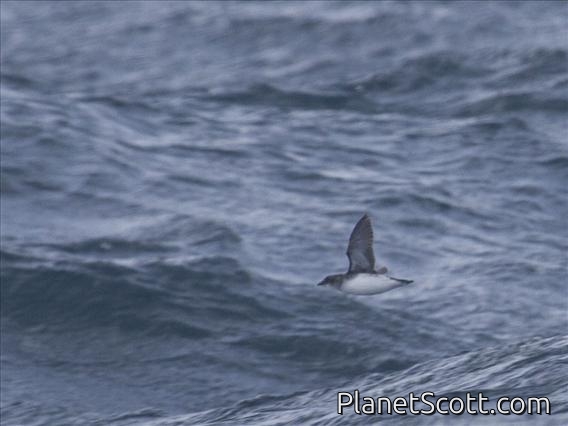
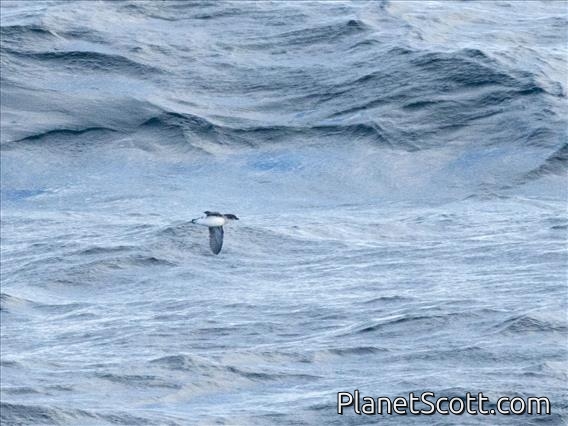
Common Diving-Petrel (Pelecanoides urinatrix)
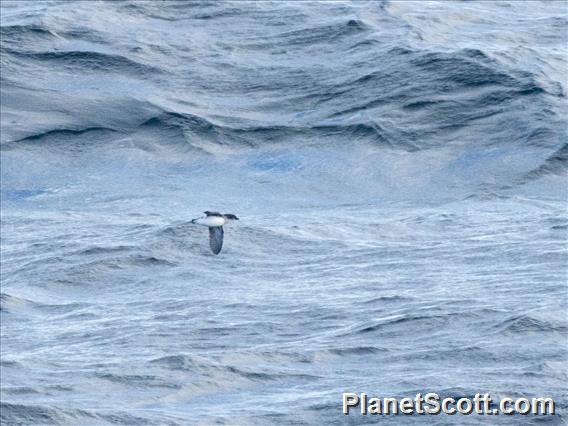

Common Diving-Petrel (Pelecanoides urinatrix)
×


Common Diving-Petrel (Pelecanoides urinatrix)
About Common Diving-Petrel (Pelecanoides urinatrix)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Tubenoses
- Family: Shearwaters and Petrels
The common diving petrel , also known as the smaller diving petrel or simply the diving petrel, is a diving petrel, one of four very similar auk-like small petrels of the southern oceans. It is native to South Atlantic islands and islands of the subantarctic southern Indian Ocean, islands and islets off New Zealand and south-eastern Australian islands.
Source: Wikipedia
Lifelists
Visits
-
2012-01-03
Stewart Island, New Zealand× -
2012-01-20
Kaikoura, New Zealand× -
2021-12-02
Drake Passage, Antarctica×