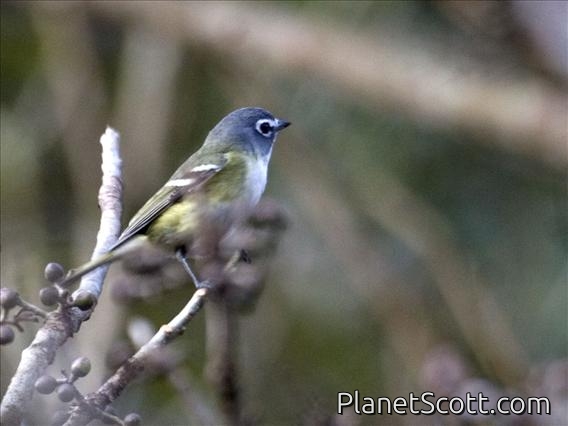
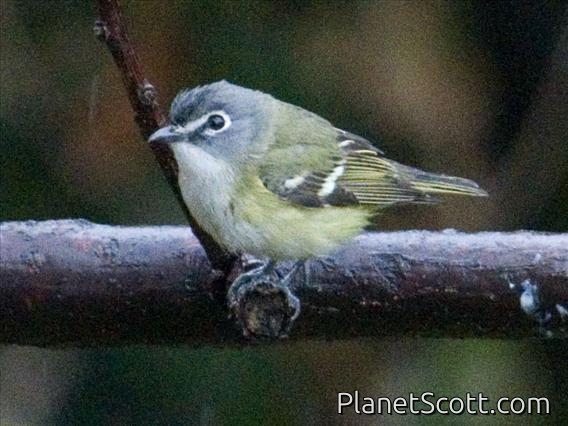
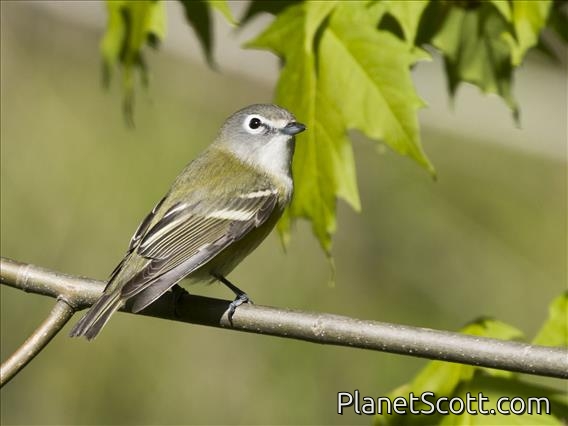
Blue-headed Vireo (Vireo solitarius)
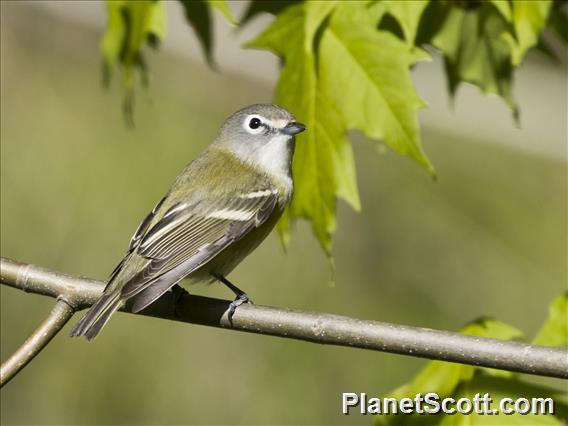

Blue-headed Vireo (Vireo solitarius)
×


Blue-headed Vireo (Vireo solitarius)
About Blue-headed Vireo (Vireo solitarius)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Perching Birds
- Family: Vireos
The blue-headed vireo is a migrating song bird found in North and Central America. There are currently two recognized subspecies that belong to the blue-headed vireo. It has a range that extends across Canada and the eastern coast of the United-States, Mexico and some of Central America. It prefers large temperate forests with a mix of evergreen trees and deciduous under growth.
Source: Wikipedia
Visits
-
2007-10-13
Xalapa, Macacuitepl Park, Mexico× -
2009-02-02
Santiago de Atitlan, Guatemala× -
2009-02-06
Copan, Honduras× -
2010-02-17
Tacambaro, Mexico× -
2013-04-19
Bolivar Peninsula, United States of America× -
×
-
×
-
×