Bewick's Wren (Thryomanes bewickii)

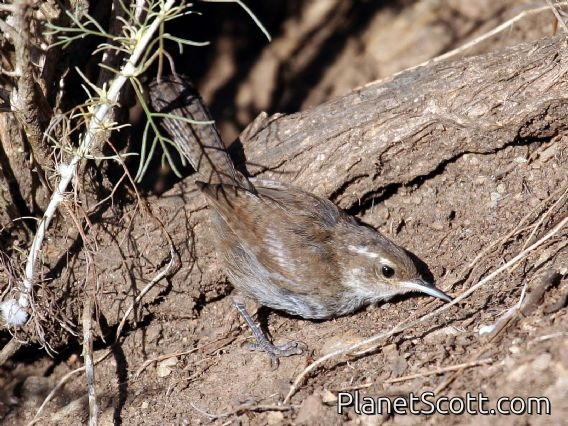
Bewick's Wren (Thryomanes bewickii)
×


Bewick's Wren (Thryomanes bewickii)
About Bewick's Wren (Thryomanes bewickii)
- Kingdom: Animals
- Phylum: Chordates
- Class: Birds
- Order: Perching Birds
- Family: Wrens
Bewick's wren is a wren native to North America. It is the only species placed in the genus Thryomanes. At about 14 cm (5.5 in) long, it is grey-brown above, white below, with a long white eyebrow. While similar in appearance to the Carolina wren, it has a long tail that is tipped in white. The song is loud and melodious, much like the song of other wrens. It lives in thickets, brush piles and hedgerows, open woodlands and scrubby areas, often near streams. It eats insects and spiders, which it gleans from vegetation or finds on the ground.
Source: Wikipedia
Trips
Visits
-
2006-08-06
Angel Island, United States of America× -
2007-04-29
Edgewood Preserve, United States of America× -
2008-04-05
Waddell Creek State Park, United States of America× -
2008-04-22
Glen Canyon Park, United States of AmericaOn the rocky outcrops near the marsh area. Not sure of the date.× -
2009-05-25
Edgewood Preserve, United States of America× -
2009-11-07
Pinnacles National Monument, United States of America× -
2010-02-21
Taxco, Mexico× -
2010-04-18
Point Reyes National Seashore, United States of America× -
2013-07-02
Yolla Bolla Wilderness, United States of America× -
2013-09-07
Mountain Lake, United States of America× -
2014-03-04
Chabot Regional Park, United States of America× -
2014-03-09
Hahamongna Watershed Park, United States of America× -
2014-03-10
Elfin Forest Preserve, United States of America× -
2014-03-22
Baker Beach, United States of America× -
2014-05-10
Cave Creek Canyon--South Fork, United States of America× -
2014-05-11
San Pedro RNCA--San Pedro House, United States of America× -
2014-06-14
Peaarson-Arastradero Preserve, United States of America× -
2014-07-12
Windy Hill OSP, United States of AmericaDid not get a great look, could have been a house wren.× -
2014-12-18
Johnston House, United States of America× -
2015-01-04
Panoche Valley, United States of America× -
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×
-
×